1950 - 1997
Highlight: Congress Passes the Current Copyright Act

On October 19, 1976, President Gerald Ford signed the Copyright Act of 1976 (Public Law 94-553), the first major revision of the copyright law since 1909. The law, with certain exceptions, went into effect on January 1, 1978, and superseded the 1909 Act. The 1976 Act extended federal copyright protection to all works, both published and unpublished, once they are fixed in a tangible form.
The term of copyright protection for new works was greatly altered, from a term of years with a renewal period, to the life of the author plus fifty years. Accordingly, the right to terminate between the initial term and the renewal term fell away, and was replaced with the right to terminate transfer after 35 years, subject to certain procedures. Congress also altered the renewal provisions for works copyrighted between January 1, 1964, and December 31, 1977, making second-term renewal automatic, and the correlating registration optional. Finally, the Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act extended the term of copyright to today’s term of the life of the author plus 70 years.
The Act also clarified the exclusion of copyright in government works to those created by an officer or employee of the United States government as part of that person’s official duties. Subsequent amendment in 1990 further clarified the role of state government agencies and employees in the copyright system, by providing that states and state employees are not immune from suit for copyright infringement under the 11th Amendment.
Since its enactment, the 1976 Act was amended multiple times to respond to rapidly changing technologies. To address the issue of new mediums of expression, Congress added protection for computer programs (December 12, 1980) and mask works fixed in semiconductor chips (November 8, 1984). To address new modes of copying and transmission of otherwise copyrighted works, Congress provided new rights in the rental, lease, or lending of a computer program (December 1, 1990) and in the public performance right for the digital transmission of sound recordings (November 1, 1995) as well as established a royalty attached to the sale of audio home recording materials for owners of sound recordings and writers and publishers of musical works (October 28, 1992). Congress also created an exemption to infringement for the use of copyrighted works by accredited nonprofit educational institutions engaged in distance education (November 2, 2002).
Finally, the 1976 Act was amended multiple times to reflect the United States’ treaty obligations with other nations. In 1989, the United States became a signatory to the 1971 Paris Act of the Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works. The Berne Convention required its signatories to extend copyright protection to architectural works and protection to visual artists certain moral rights of attribution and integrity. On December 1, 1990, Congress passed the Visual Artist Rights Act and Architectural Works Copyright Protection Act to provide these protections through the copyright law. Then, on December 8, 1993, the North American Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act was enacted to extend copyright protection to certain motion pictures first fixed without copyright notice in Canada or Mexico between January 1, 1978, and March 1, 1989.
-
International Copyright
-
History of the Copyright Office
-
Copyright Law
-
Copyright in the Courts
-
Fifth Register of Copyrights Is Appointed
September 12, 1951

Arthur Fisher taught constitutional law, practiced law, and served in the government before joining the Copyright Office staff.
-
Recording and Performing Rights for Nondramatic Literary Works
January 1, 1953
Recording and performing rights are extended to nondramatic literary works.
-
Supreme Court Rules on Artworks Embodied in "Useful Articles"
March 8, 1954
In "Mazer v. Stein," the Supreme Court holds that works of art embodied in useful articles may be copyrighted.
-
Universal Copyright Convention Takes Effect
September 16, 1955
The Universal Copyright Convention, a multilateral international copyright treaty, enters into force. President Dwight Eisenhower signed the treaty on November 5, 1954.
-
Sixth Register of Copyrights Is Appointed
December 24, 1960

Abraham Lewis Kaminstein served in the Copyright Office for 13 years before his appointment as Register, including service as the first chief of the Examining Division when it was formed in 1947.
-
First Stopgap Measure Introduced to Keep Copyrights from Expiring
September 19, 1962
The first of nine special acts is introduced to extend subsisting renewal copyrights pending a general copyright law revision.
-
Seventh Register of Copyrights Is Appointed
September 1, 1971

George D. Cary began working in the Copyight Office as a lawyer in 1947 and served for 10 years as deputy Register before his appointment as Register.
-
Sound Recordings Get Federal Protection
February 15, 1972
Congress extends federal protection to sound recordings fixed and first published on or after February 15, 1972. Recordings fixed earlier remain under the protection of state laws.
-
First Sound Recording Registrations Are Made
February 16, 1972
"Music from the Mother Church," registered by the Christian Science Publishing Society, is among several sound recording registrations entered on February 16, 1972.
-
Eighth Register of Copyrights Is Appointed
November 19, 1973

Barbara Ringer, who joined the Copyright Office staff in 1949 as an examiner, is the first woman to serve as Register.
-
U.S. Becomes Party to the Geneva Phonograms Convention
March 10, 1974
The membership of the United States in the Convention for the Protection of Producers of Phonograms Against Unauthorized Duplication of Their Phonograms (Geneva, 1974) takes effect.
-
United States Becomes Party to Revised UCC Treaty
July 10, 1974
The United States joins the 1971 revision of the Universal Copyright Convention.
-
Copyright Act of 1976
October 19, 1976
President Gerald Ford signs the fourth general revision of the copyright law. Federal protection is extended to all works, both unpublished and published, once they are fixed in a tangible form. The copyright term for works created on or after January 1, 1978, the effective date of the law, is the life of an author plus 50 years.
-
Fourth General Revision of Law Takes Effect
January 1, 1978

The principal provisions of the 1976 Copyright Act take effect.
-
Ninth Register of Copyrights Is Appointed
June 2, 1980
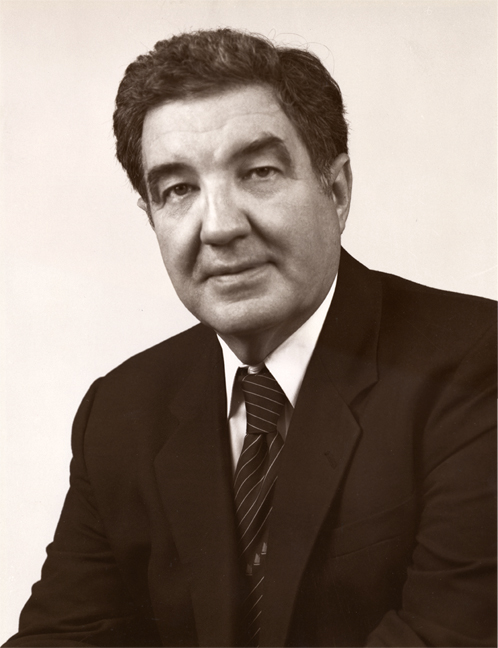

David L. Ladd is the first Register who had also served as Commissioner of Patents.
-
Computer Programs Are Copyrightable
December 12, 1980

The law is amended to confirm the copyrightability of computer programs.
-
Supreme Court Rules on Home Videorecording
January 17, 1984
In "Sony Corp. of America v. Universal City Studios, Inc.," the Supreme Court rules that a videocassette manufacturer cannot be held liable for copyright infringement solely on the basis of distributing a product capable of substantial noninfringing uses.
-
"Mask Works" Get Federal Statutory Protection
November 8, 1984
The Semiconductor Chip Protection Act of 1984 establishes a new type of intellectual property protection for mask works fixed in semiconductor chips and charges the Copyright Office with responsibility for registering mask works.
-
Tenth Register Is Appointed
September 23, 1985
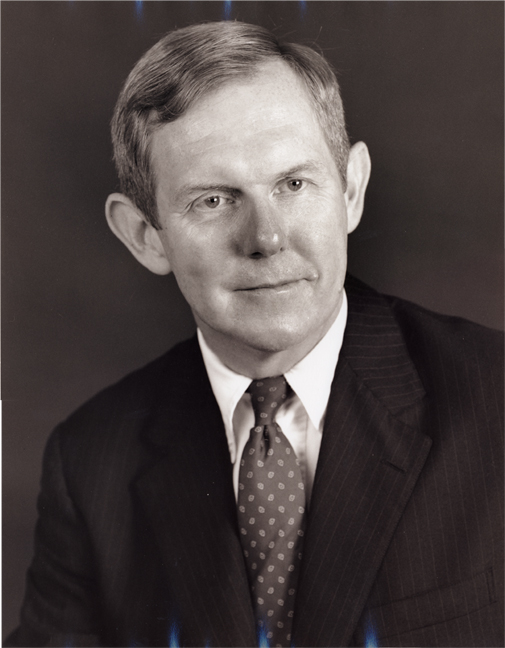

Ralph Oman was chief counsel to the U.S. Senate Committee on the Judiciary's Subcommittee on Patents, Copyrights, and Trademarks immediately before his appointment as Register.
-
United States Joins Berne Convention
March 1, 1989
The United States adheres to the 1971 Paris Act of the Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, the oldest and most extensive multilateral international copyright treaty.
-
Supreme Court Addresses "Work Made for Hire"
June 5, 1989
In "Community for Creative Non-Violence v. Reid," the U.S. Supreme Court interprets the meaning of “work made for hire” under copyright law.
-
States Not Immune from Copyright Lawsuits
November 15, 1990
Section 511 is added to the copyright law, providing that states and state employees and instrumentalities are not immune under the 11th Amendment from suit for copyright infringement.
-
Computer Software Rentals
December 1, 1990
The Computer Software Rental Amendment Act takes effect, granting the owner of copyright in computer programs the exclusive right to authorize or prohibit the rental, lease, or lending of the program for direct or indirect commercial purposes.
-
Protection Extended to Architectural Works
December 1, 1990
Copyright protection is extended to architectural works.
-
Moral Rights for Visual Artists
December 1, 1990
The Visual Artists Rights Act of 1990 grants to visual artists certain moral rights of attribution and integrity.
-
Copyright Protection Tied to Creative Originality
March 27, 1991
In "Feist Publications, Inc. v. Rural Telephone Service," the Supreme Court finds a white pages telephone directory to be uncopyrightable, holding creative originality a requirement for copyright protection.
-
Renewal Registration Made Optional
June 26, 1992
Renewal registration becomes optional. Works copyrighted between January 1, 1964, and December 31, 1977, are automatically renewed even if registration is not made.
-
Royalties Introduced on Sale of Digital Audio Recording Devices
October 28, 1992
The Audio Home Recording Act provides for royalties to performers and copyright owners of sound recordings and to writers and publishers of musical works upon the manufacture and sale of digital audio recording devices and media.
-
Copyright Restoration of Certain Motion Pictures
January 1, 1994
The North American Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act extends copyright protection to certain motion pictures first fixed in Canada or Mexico between January 1, 1978, and March 1, 1989, and published without a copyright notice.
-
Eleventh Register of Copyrights Is Appointed
August 7, 1994

Marybeth Peters joined the Copyright Office staff in 1966 as a music examiner and advanced to positions at all levels of the Office. She had the longest tenure of any Register except Thorvald Solberg, the first Register.
-
Copyright Restored to Public Domain Works
December 8, 1994
The Uruguay Round Agreements Act restores copyright to certain foreign works under protection in the source country but in the public domain in the United States.
-
World Trade Organization Agreement Addresses Copyright in the Context of International Trade
January 1, 1995
The World Trade Organization’s Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement enters into force. The WTO TRIPS Agreement sets forth obligations related to intellectual property rights, including copyright and enforcement measures, in the context of a multilateral trade agreement.
-
Copyright Office Publishes List of Certain Restored Motion Pictures
February 13, 1995
The Copyright Office published a list of 345 titles for which Statements of Intent to Restore Copyright in the United States were filed under the terms of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its implementing statute. Potential owners of eligible motion pictures who filed a complete and timely Statement of Intent with the Copyright Office restored copyright protection in those works effective January 1, 1995. For the list of motion pictures, see the Office’s announcement.
-
Digital Performance Right for Sound Recordings
November 1, 1995
The Digital Performance Right in Sound Recordings Act of 1995 creates a public performance right in sound recordings applicable to digital transmissions.
-
International Treaties Address Digital Technologies
December 20, 1996
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Copyright Treaty and the WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty are adopted to deal with the protection of works, sound recordings, and performances in sound recording and the rights of authors, producers of sound recordings and performers in the digital environment. The treaties enter into force in 2002.
